11:15 PM Safe work with hydrogen sulfide (H2S) in the oil fields |
 Hydrogen sulfide is a highly flammable hazardous gas that occurs naturally in crude petroleum and natural gas. It also is present in sewage, created through the breakdown of organic matter, and can cause negative health effects when inhaled. Hydrogen sulfide is heavier than air so it tends to be more highly concentrated in low-lying areas that are poorly ventilated, such as basements, manholes, sewer lines, and underground telephone or electrical vaults. Hydrogen sulfide is a highly flammable hazardous gas that occurs naturally in crude petroleum and natural gas. It also is present in sewage, created through the breakdown of organic matter, and can cause negative health effects when inhaled. Hydrogen sulfide is heavier than air so it tends to be more highly concentrated in low-lying areas that are poorly ventilated, such as basements, manholes, sewer lines, and underground telephone or electrical vaults. The reason it cognizance or disregarded by worker or boss, the risk of exposure to hydrogen sulfide is associated with individual and collective catastrophic incidents. Dermal, respiratory, and eye chronic exposure to low concentration (non-lethal) to hydrogen sulfide causes symptoms and risks can be summarized as follows:
In general emergence of some or all these symptoms on worker be reflected in work product quality and its economy so all workers and bosses who work in oil and gas field must know the concentration of hydrogen sulfide gas in the field and the risk of exposure and know required safety procedure to ensure the work and worker. Define of hydrogen sulfideHydrogen sulfide is a colorless, flammable, extremely hazardous gas with a "rotten egg” smell, heavier than air so it exists in lowland when it leaking. It occurs naturally in crude petroleum, natural gas, and hot springs. Industrial activities that can produce the gas include petroleum/natural gas drilling and refining, wastewater treatment, coke ovens, tanneries, and Kraft paper mills. Hydrogen sulfide can also exist as a liquid compressed gas. This following table shows its physical characteristics: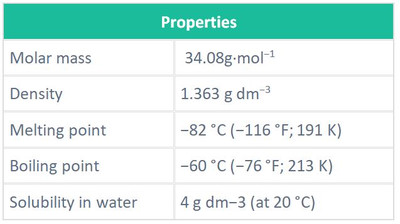 Disclosed hydrogen sulfideThey may not rely on the sense of smell to detect hydrogen sulfide because of its gravity. There are several ways to detect it (Methylene blue, Gas and liquid chromatography, Color of flame and Gas detector).Level of risk and preventive action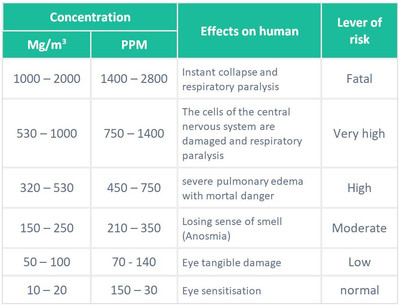 Avoiding exposureBefore entering areas where hydrogen sulfide may be present, have a qualified person test the air. This will indicate whether fire or explosion precautions are necessary.If the gas is present, the area should be ventilated. If the gas cannot be removed, workers should be equipped with proper personal protective, rescue and communication equipment. A self-contained breathing apparatus is required in spaces with a concentration higher than 100 parts per million. Health effects of hydrogen sulfideHydrogen sulfide a mucous membrane and respiratory tract irritant; pulmonary edema, which may be immediate or delayed, can occur after exposure to high concentrations.
|
|
|
| Total comments: 0 | |